这是我参与8月更文挑战的第14天,活动详情查看:8月更文挑战
Deep Learning with Python
这篇文章是我学习《Deep Learning with Python》(第二版,François Chollet 著) 时写的系列笔记之一。文章的内容是从 Jupyter notebooks 转成 Markdown 的,你可以去 GitHub 或 Gitee 找到原始的 .ipynb 笔记本。
你可以去这个网站在线阅读这本书的正版原文(英文)。这本书的作者也给出了配套的 Jupyter notebooks。
本文为 第8章 生成式深度学习 (Chapter 8. Generative deep learning) 的笔记之一。
8.2 DeepDream
DeepDream 是一种让机器修改图像技术,它利用卷积神经网络,可以作出很迷幻的图像:

由于 DeepDream 用的 CNN 是在 ImageNet 上训练的,而 ImageNet 里有大量的动物图片,所以,DeepDream 生成的图像里有很多动物、动物的一部分的伪影。
DeepDream 使用的算法与卷积神经网络过滤器可视化技术很类似。回忆一下,卷积神经网络过滤器可视化所做的操作是:反向运行卷积神经网络,从一张带随机噪点的空白图像输入,做梯度上升,使某过滤器激活最大化。
DeepDream 与过滤器可视化的主要区别在于:
- 在 DeepDream 中,我们尝试将所有层的激活最大化,而不只是某一层,这样,会有大量的可视化特征混合在一起——生成更加迷幻的图像。
- 从一张现有的图像开始,而不是从随机噪点的输入开始,这样生成的图像中会包含输入图像中已存在的视觉模式,并以将其中的一些元素扭曲——生成更加迷幻的图像。
- 输入图像会在不同的尺度上进行处理——这些尺度称为「八度」(octave),这可以提高输出的质量。
用 Keras 实现 DeepDream
在开始之前,我们需要关闭 Tensorflow 2.x 的及时执行模式,参考 tensorflow #33135。
import tensorflow as tf
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
复制代码然后第一步,选定一个在 ImageNet 上预训练的卷积神经网络:VGG16、Inception、ResNet50 等等都可以。实践证明,Inception 可以生成的比较好,所以这里我们使用 Keras 内置的 Inception V3 模型。
加载预训练的 Inception V3 模型:
from tensorflow.keras.applications import inception_v3
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
K.set_learning_phase(0)
model = inception_v3.InceptionV3(weights='imagenet', include_top=False)
复制代码接下来定义损失——需要用梯度上升最大化的量。DeepDream 中,我们要同时将多个层的所有过滤器激活最大化。具体的实现是:对一组靠近顶部的层激活的 L2 范数进行加权求和,然后求出这个值的最大化。层的选择、以及权重分配对生成的结果影响很大:
- 靠近底部的层会生成基本的几何图案;
- 靠近顶部的层会生成能够看出某些物品的图像(ImageNet 中的图案,比如鸟或狗)
输出 Inception V3 模型的结构(可以用 tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model)),在其中随便选几个层,这里选择了 mixed4、mixed5、mixed6 和 mixed7。
把这些要用的层写到 DeepDream 配置里:
layer_contributions = {
'mixed4': 0.0,
'mixed5': 3.0,
'mixed6': 2.0,
'mixed7': 1.5,
}
复制代码然后我们需要求对于这些被选中层的损失。定义需要最大化的损失:
layer_dict = dict([(layer.name, layer) for layer in model.layers])
loss = K.variable(0.)
for layer_name in layer_contributions:
coeff = layer_contributions[layer_name]
activation = layer_dict[layer_name].output
scaling = K.prod(K.cast(K.shape(activation), 'float32'))
# loss += coeff * K.sum(K.square(activation[:, 2: -2, :])) / scaling
# 应该用下面的代码?。参考:https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-with-python-notebooks/issues/43
loss = loss + coeff * K.sum(K.square(activation[:, 2: -2, :])) / scaling
复制代码对损失做梯度上升:
dream = model.input
grads = K.gradients(loss, dream)[0]
grads /= K.maximum(K.mean(K.abs(grads)), 1e-7)
outputs = [loss, grads]
fetch_loss_and_grads = K.function([dream], outputs)
def eval_loss_and_grads(x):
outs = fetch_loss_and_grads([x])
loss_value = outs[0]
grad_values = outs[1]
return loss_value, grad_values
def gradient_ascent(x, iterations, step, max_loss=None):
for i in range(iterations):
loss_value, grad_values = eval_loss_and_grads(x)
if max_loss is not None and loss_value > max_loss:
break
print(f' loss value at {i}: {loss_value}')
x += step * grad_values
return x
复制代码最后,实现 DeepDream 算法:先定义一个尺度(scales,也叫做八度,octaves)列表,里面包含要处理的图像。后一个尺度的图像比前一个放大一定的倍数。DeepDream 要按照这个列表从最小到最大,在当前尺度运行梯度上升,然后将得到的图像放大。放大之后,图像会变得模糊,所以还要将丢失的细节重新注入到图像中。

一些辅助函数:
import scipy
import imageio
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
def resize_img(img, size):
img = np.copy(img)
factors = (1,
float(size[0]) / img.shape[1],
float(size[1]) / img.shape[2],
1)
return scipy.ndimage.zoom(img, factors, order=1)
def save_img(img, fname):
pil_img = deprocess_image(np.copy(img))
# scipy.misc.imsave(fname, pil_img)
imageio.imsave(fname, pil_img)
复制代码打开图像,改变图像大小,并将图像格式转换为 Inception V3 模型能够处理的张量:
def preprocess_image(image_path):
img = image.load_img(image_path)
img = image.img_to_array(img)
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
img = inception_v3.preprocess_input(img)
return img
复制代码将一个张量转换为有效图像:
def deprocess_image(x):
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x = x.reshape((3, x.shape[2], x.shape[3]))
x = x.transpose((1, 2, 0))
else:
x = x.reshape((x.shape[1], x.shape[2], 3))
x /= 2.
x += 0.5
x *= 255.
x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
return x
复制代码在多个连续尺度上运行梯度上升:
import numpy as np
step = 0.01 # 梯度上升的步长
num_octave = 3 # 尺度个数
octave_scale = 1.4 # 两个尺度的大小比例
iterations = 20 # 在每个尺度上运行梯度上升的步数
max_loss = 10. # 损失上升的太大时中止梯度上升,以免得到丑陋的伪影
base_image_path = './img.png'
img = preprocess_image(base_image_path)
original_shape = img.shape[1:3]
successive_shapes = [original_shape]
for i in range(1, num_octave):
shape = tuple([dim // (octave_scale ** i)
for dim in original_shape])
successive_shapes.append(shape)
successive_shapes = successive_shapes[::-1]
original_img = np.copy(img)
shrunk_original_img = resize_img(img, successive_shapes[0])
for shape in successive_shapes:
print('Processing image shape', shape)
img = resize_img(img, shape)
img = gradient_ascent(img,
iterations=iterations,
step=step,
max_loss=max_loss)
upscaled_shrunk_original_img = resize_img(shrunk_original_img, shape)
same_size_original = resize_img(original_img, shape)
lost_detail = same_size_original - upscaled_shrunk_original_img
img += lost_detail
shrunk_original_img = resize_img(original_img, shape)
save_img(img, fname=f'dream_at_scale_{shape}.png')
save_img(img, fname='final_dream.png')
复制代码最终得到的结果:

可以看到 DeepDream 在 final_dream 图片里,画上了几只狗?。
注:由于 Inception V3 原始训练的尺寸的缘故,这里实现的 DeepDream 实现在尺寸介于 300×300 和 400×400 之间的图像上能够得到更好的结果,不过这不是严格的限制,任何尺寸的都是可以的。
注:使用 TensorfFlow 2 的 eager 模式,也可以很容易地实现一个更好的 DeepDream,详见这篇 TensorFlow 的官方教程。
















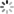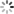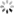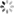




![[桜井宁宁]COS和泉纱雾超可爱写真福利集-一一网](https://www.proyy.com/skycj/data/images/2020-12-13/4d3cf227a85d7e79f5d6b4efb6bde3e8.jpg)

![[桜井宁宁] 爆乳奶牛少女cos写真-一一网](https://www.proyy.com/skycj/data/images/2020-12-13/d40483e126fcf567894e89c65eaca655.jpg)